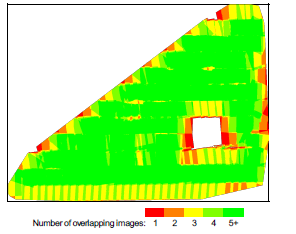
Pix4d is an image processing software that is based on automatically finding thousands of common points between images. When the same common points (keypoints) are found on multiple images the, program generates a 3D point. In order to create highly accurate 3D images, images must maintain high amounts of overlap to create as many 3D points as possible. It is recommended by Pix4d that at least 75% frontal and 60% side overlap is maintained.
Pix4dmapper 3.1 Usermanual
When mapping terrain such as forest and dense vegetation, flat terrain with agriculture fields, and areas of snow and sand a minimum of 85% frontal and 70% side overlap is recommended for quality map construction in Pix4d. In many cases camera settings, such as exposure, must be adjusted to receive quality images. Pix4d can process multiple flights by overlapping images from both flights. Both flights must be taken at a similar altitude. Pix4d can also process oblique images. For the user to get high quality maps from oblique images, the user must take images with their camera at multiple different angles. Pix4d does not require Ground Control points to create accurate georeferenced maps. The program will automatically do this with the coordinates that are tied to the images. It is recommended that GCP's are taken of the study area and put into Pix4d to create the most accurate map possible but is not required. If the pilot is conducting multiple flights of the area it is important that they are maintaining the same height and overlap for each flight. This will ensure the best possible data. After inputting and processing the images a quality report is created that includes details about the processing such as, summaries, quality checks, calibrations, maps, and information of the data.
How to Use the Software:
To begin processing in Pix4d the user must connect the program to where they want to save and what to call the new project.
The user must then import their images
Once the images are imported into the user must confirm or change, image coordinate system, geolocation and camera settings. Camera setting are important to have right to allow for proper image processing.
In this case the camera shutter model was set to a Global Default and was changed to a Linear Rolling Shutter.
The next step is to confirm the output coordinate system and GCP coordinate system and select the type of processing that needs to be done. In this case we selected for Pix4d to create 3D Maps.
When finished inputting the data the user gets to a screen that allows them to start the processing. The user then sets his processing options and selects to only do the initial process. If the user leaves, Initial Processing, Point Cloud and Mesh, and DMS, Orthomosaic and Index selected it will process all three parts while doing an initial process for each part. This wastes time so it is advised to run the initial process, then run #2 and #3 together.
After processing the user will get reports for each process as well as the map. All the user needs to do to view the map is turn cameras off in the layers section and turn on triangle meshes. This will result in a map similar to below.
After processing the user will get reports for each process as well as the map. All the user needs to do to view the map is turn cameras off in the layers section and turn on triangle meshes. This will result in a map similar to below.
Maps/Data:
After the processing, Pix4d creates a report with lots of useful information. The first page of the quality reports shows a summary, quality check of processing results, and a preview of the maps that are created.
The .tif files created in Pix4d can be imported into a geodatabase in ArcMap and created into visually appealing maps. The map below is a Digital Surface model and a mosaicked image of the mine the data was taken from. The map on the right shows the height of different objects in a color scale model and the map on the left shows the visible band image of the area.
Unfortunately the data taken from this lab was incorrect. There was an issue with the camera and how it tied in elevation data to the images. When using the identify tool in ArcMap it says that the elevation is around 100m above mean sea level. In reality the elevation if this area is more in the area of 220+m above sea level. This is a severe mistake in the data means this data cannot be used.
This issue of incorrect elevation will be solved in the next lab, processing data in Pix4D with GCP's.
First Impressions of Pix4d:
At first impression this software is easy to use and can be very beneficial for many applications in the UAS world. Taking drone imagery then turning it into a georeferenced 3D map without Pix4d would require extensive knowledge of different programs and algorithms. Pix4d allows for a user to quickly create high quality 3D maps in a short period of time. To create an image that is more spatially accurate Ground Control Points should have been manually put in and taken of the area then tied to the imagery. Pix4d automatically creats GCP's from the locations on the images but this is not completely accurate. This first look at Pix4d was a great introduction to 3D mapping from UAS data. There is much more to learn about image processing in Pix4d.
Conclusions:
Overall, Pix4d is a very useful tool in importing and processing large amounts of images from a UAS platform. It streamlines the workflow allowing the user more time for analyzing the data to gain contextual insight and less time processing and creating maps and images. Mistakes can be made using this software so users must take caution. A person who does not know a lot about mapping and datums and lacks GIS experience could have taken this data set and used in for pile volumetrics. This would have led to severely wrong numbers that would lead to an expensive lawsuit.











No comments:
Post a Comment